

If the two remaining bonds on the nitrogen atom are attached to hydrogen.
metal amide, an ionic compound ("salt") with the azanide anion H 2N − (the conjugate base of ammonia) or to a derivative thereof R 2N −. The amide functional group has an nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl carbon atom. Voiceover: Another carboxylic acid derivative is the amide functional group, and you'll hear many different ways to pronounce this functional group. cyclic amide or lactam, a cyclic compound with the amide group –C(=O)N– in the ring. Commonly used to relieve pain or reduce a fever, Tylenol is a well-known over-the-counter. functional group has a carbonyl group joined to a nitrogen atom from ammonia or an amine. Tylenol is very common it might be sitting in your medicine cabinet right now. The dash means it is Functional Group like -R means hydrocarbyl functional group, -COOH means carboxylic acid functional group, etc. What you have shown in the question is bond structure of 2° amide, which can be obtained by removing 1 hydrogen from 1° amide. amide group, a functional group –C(=O)N= consisting of a carbonyl adjacent to a nitrogen atom. The functional group of an amine is a nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons and with one, two, or three alkyl or aryl groups attached. The bond structure of 1° amides is as shown in the figure. sulfonamides, where E = sulfur, namely RS(=O) 2NR 2. phosphoramides, where E = phosphorus, such as R 2P(=O)NR 2. It is tempting to call it an alcohol group. The structure of acetaminophen is The group at the top of the molecule is a hydroxyl group. > A functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that gives rise to the characteristic chemical reactions of the molecule. 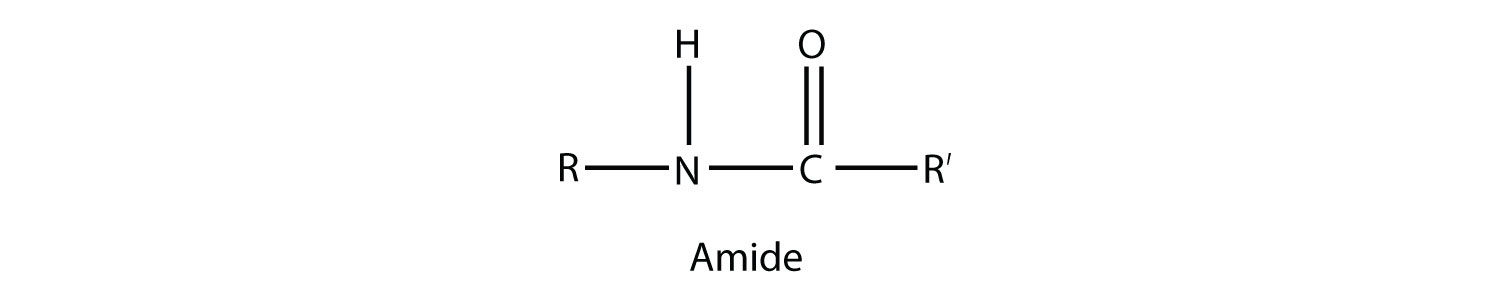 carboxamides, or organic amides, where E = carbon, with the general formula RC(=O)NR 2. The functional groups in acetaminophen are hydroxyl, aromatic ring, and amide. The four nitrogen atoms in the caffeine molecule result in either amines or amide groups depending on whether or not they are bound to a carbonyl, which is a carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom. It is a derivative of an oxoacid R nE(=O) xOH with an hydroxy group –OH replaced by an amine group –NR 2. By comparing a list of functional groups to the structure of caffeine, it is possible to find one alkene, two amides and two amines. A N atom which is bonded to a CO (carbonyl) group is called an amide. In chemistry, the term amide ( / ˈ æ m aɪ d/ or / ˈ æ m ɪ d/ or / ˈ eɪ m aɪ d/) is a compound with the functional group R nE(=O) xNR 2, where n and x may be 1 or 2, E is some element, and each R represents an organic group or hydrogen. 1.62 Functional groups containing one (or more) single bonded O atoms a) Alcohol. Structures of three kinds of amides: an organic amide (carboxamide), a sulfonamide, and a phosphoramide.
carboxamides, or organic amides, where E = carbon, with the general formula RC(=O)NR 2. The functional groups in acetaminophen are hydroxyl, aromatic ring, and amide. The four nitrogen atoms in the caffeine molecule result in either amines or amide groups depending on whether or not they are bound to a carbonyl, which is a carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom. It is a derivative of an oxoacid R nE(=O) xOH with an hydroxy group –OH replaced by an amine group –NR 2. By comparing a list of functional groups to the structure of caffeine, it is possible to find one alkene, two amides and two amines. A N atom which is bonded to a CO (carbonyl) group is called an amide. In chemistry, the term amide ( / ˈ æ m aɪ d/ or / ˈ æ m ɪ d/ or / ˈ eɪ m aɪ d/) is a compound with the functional group R nE(=O) xNR 2, where n and x may be 1 or 2, E is some element, and each R represents an organic group or hydrogen. 1.62 Functional groups containing one (or more) single bonded O atoms a) Alcohol. Structures of three kinds of amides: an organic amide (carboxamide), a sulfonamide, and a phosphoramide.








